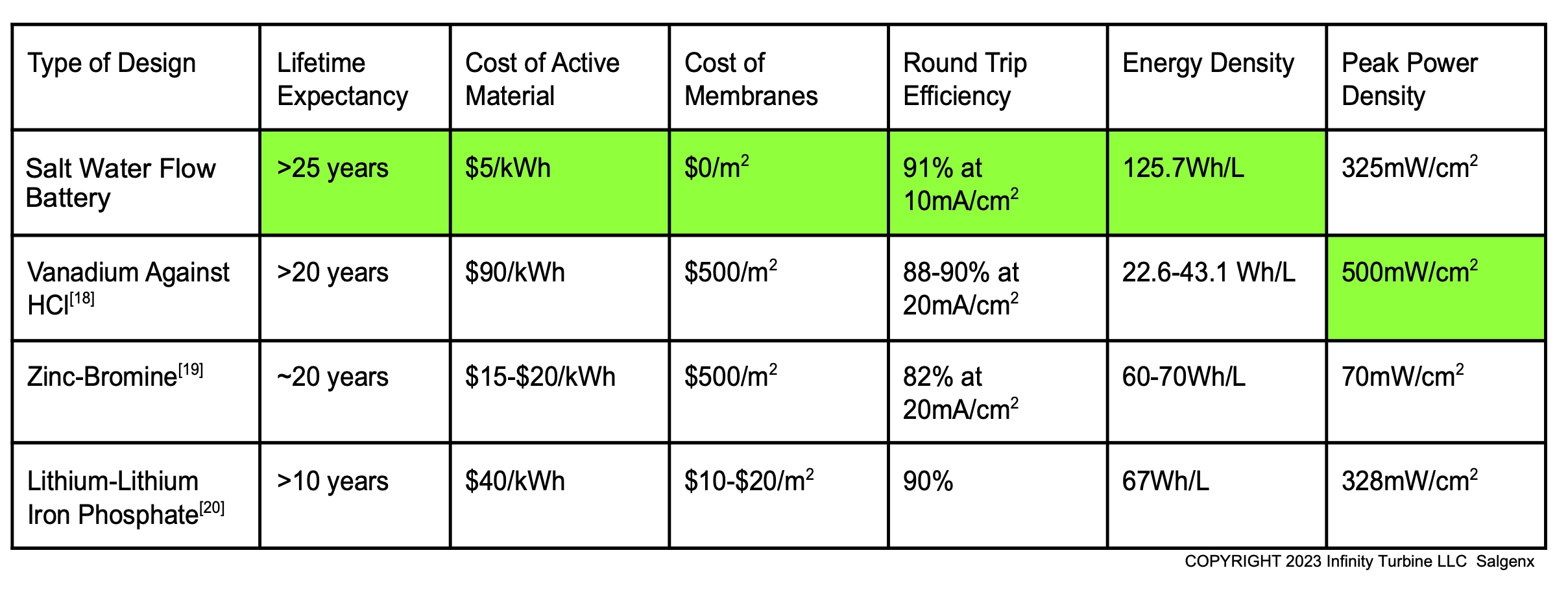
Flow Battery Tech Comparison Chart

Salgenx LLC • Design • Develop • Analysis TEL: 1-608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com
3 MWh Grid Scale Saltwater Flow Battery that is Self Healing More Info
|
Fastest Path to a 3 MWh Grid-Scale Saltwater Flow Battery: Zinc-Chlorine vs NTP-Based Architectures Which saltwater flow battery chemistry reaches grid-scale commercialization first? This article compares zinc metal and NTP-based chlorine flow batteries across cost, efficiency, manufacturing complexity, and bankability to determine the fastest and most cost-effective path to a 3 MWh system.IntroductionGrid-scale energy storage increasingly demands systems that are safe, low-cost, scalable, and free from constrained materials. Saltwater flow batteries, particularly chlorine-based systems, have re-emerged as a compelling alternative to lithium-ion due to their use of abundant materials, non-flammable electrolytes, and long cycle life.Recent research has demonstrated a membrane-free chlorine flow battery architecture with exceptionally low projected material cost. Within this platform, two negative electrode strategies emerge as candidates for commercialization:1. Zinc metal negative enabled by a ZnCl2 additive2. NaTi2(PO4)3 (NTP) intercalation negative without zinc additiveThis article evaluates both approaches for a 3,000 kWh grid-scale containerized system and determines which offers the fastest, lowest-risk, and most cost-effective path to market.System Architecture OverviewBoth battery variants share a common core architecture:• Aqueous NaCl electrolyte• Chlorine redox at the positive electrode• Closed-loop chlorine handling using an immiscible organic carrier• Membrane-free stack design• Modular stacks arranged into a roughly 900 V DC busThe primary difference lies in the negative electrode chemistry and its implications for voltage, efficiency, manufacturing, and cost.Option A: Zinc-Chlorine Flow Battery with ZnCl2 AdditiveElectrochemistry• Positive: Cl2 / Cl minus• Negative: Zn2 plus / Zn metal• Nominal cell voltage: approximately 1.9 VAdding ZnCl2 to the electrolyte enables reversible zinc plating and stripping, replacing the need for a solid-state intercalation cathode.Manufacturing and Commercial Advantages• Zinc metal is a commodity material available as sheet, foil, or plated substrates (it is also available at Home Depot).• Electrode fabrication is simple and scalable• No high-temperature ceramic synthesis or vapor deposition steps• Aligns with historical zinc-halogen battery manufacturing experienceThe zinc electrode can be designed as a serviceable component, enabling predictable maintenance rather than end-of-life replacement.Risks• Zinc dendrite formation must be controlled through current density, flow design, and electrolyte management• Coulombic efficiency must be validated at scaleOption B: Chlorine Flow Battery with NTP CathodeElectrochemistry• Positive: Cl2 / Cl minus• Negative: NaTi2(PO4)3 (NTP)• Nominal cell voltage: approximately 1.8 VNTP is a NASICON-type insertion material offering good rate capability and stable cycling.Manufacturing and Commercial Challenges• NTP synthesis requires high-temperature calcination• Conductive carbon coating is necessary, typically involving additional thermal processing or vapor deposition• Powder processing and electrode fabrication add complexity and capital costWhile technically elegant, NTP introduces a more complex supply chain and slower ramp to volume production.Costed BOM Comparison for a 3 MWh ContainerUsing the Nature Communications estimate of approximately $5 per kilowatt-hour as a floor for active materials, and legacy zinc-chlorine plant data as a balance-of-plant sanity check, the following system-level costs emerge:• Zinc-Chlorine system total installed cost: approximately xxxxx dollars• NTP-based system total installed cost: approximately xxxxx dollarsThis corresponds to:• Zinc system: approximately xx dollars per kWh installed• NTP system: approximately xxx dollars per kWh installedIn both cases, balance-of-plant, power electronics, and safety systems dominate total cost, not the electrochemistry itself.Efficiency and Cost-Per-Delivered-kWhEfficiency must be evaluated alongside capital cost to assess true economic performance.• NTP-based systems have demonstrated laboratory-scale energy efficiency exceeding 90 percent• Zinc-based systems typically operate in the 70 to 75 percent range when system parasitics are includedWhen adjusted for efficiency:• Zinc system effective cost per delivered kWh: approximately xx to xx dollars• NTP system effective cost per delivered kWh: approximately xx to xxx dollarsThis indicates that while NTP offers higher efficiency, the zinc system compensates with lower upfront cost and faster manufacturability.Fastest Path to Market AssessmentFrom a commercialization standpoint, the decisive factors are manufacturability, supply chain simplicity, and execution risk.• Zinc metal electrodes eliminate the need for specialty ceramic powders and carbon coating processes• Anodes are already mass-produced industrial components• The zinc system supports a service-based maintenance model familiar to utilitiesThe NTP system, while attractive for future optimization, introduces additional process steps that slow time to first deployment.Commercial VerdictFor a first-generation, grid-scale saltwater flow battery:• The zinc-chlorine system with ZnCl2 additive is the fastest to market• It offers the lowest installed cost• It presents the least manufacturing risk• It enables early revenue and field validationThe NTP-based system is best positioned as a second-generation or premium offering once manufacturing scale and customer confidence are established.ConclusionSaltwater flow batteries based on chlorine chemistry present a credible, scalable alternative to lithium-ion for long-duration grid storage. Between the two leading negative electrode options, zinc metal offers the most direct path to commercialization for a 3 MWh containerized system. Its simplicity, cost advantage, and alignment with existing industrial practices outweigh the efficiency advantage of NTP in early deployments.A dual-track strategy is recommended: deploy zinc-based systems first to capture market share and operational data, while continuing development of NTP-based systems for future high-efficiency products.References1. Hou et al. High Energy and Low Cost Membrane Free Chlorine Flow Battery. Nature Communications, 2022.2. Detroit Edison and Energy Development Associates. Zinc Chlorine Battery Utility Study and Cost Analysis, 1976 to 1977.3. Bard and Faulkner. Electrochemical Methods Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley.4. U.S. Department of Energy. Grid Energy Storage Technology and Cost Characterization Reports. |

Flow Battery Tech Comparison Chart |

|
Why Salt Water may be the Future of Batteries There’s no shortage of solutions to the world’s need for renewable energy storage, but there is a shortage of accessible and cheap resources to use for those solutions. Lithium and vanadium aren't limitless, so what about regular, run-of-the-mill salt? Redox flow batteries, or RFBs, can exploit the abundance of elements like sodium and iron. One U.S. company already has salt water batteries ready to go, with at least two others developing iron flow variations built to effectively run on rust. They promise to last longer and be far cheaper than the competition. So, what happens if we go with the flow?Why Salt Water may be the Future of Batteries Vanadium Redox Flow Battery versus Salgenx Saltwater Flow Battery Comparison |

|
News: No Tariffs or Duties or VAT for USA Produced Batteries | CATL is Moving to Sodium Build in the country that you are selling, to avoid most tariffs and taxes.CATL is Switching to SIB: CATL, the worlds largest battery manufacturer (40 percent of the market) is switching to sodium ion batteries (SIB). This battery can operate as low as -40 C and will be competitive with lithium based batteries. The leading edge manufacturers are moving to sodium tech.
|

Infinity Turbine Radial Outflow Turbine Generator which can be used simultaneously as a heat pump |
As a simultaneous Thermal Storage Device Considered a hybrid between a standard flow battery and a thermal storage device, the battery provides simultaneous heat or cold liquid storage as well as electrical energy storage.The Cogen Battery has a variety of applications which include:-storage of thermal energy (heating or cooling) from unused thermal resources-storage of electrical power for backup power and grid strength-utility grid power rate mining opportunities to store off-peak low cost power for later use during demand (on-peak) hours-storage of thermal energy for Organic Rankine Cycle (ORC) power production while simultaneously storing the electrical output from the turbine generator-using off-peak low cost power to make heating and cooling for later use-reducing peak demand utility rates by peak energy shaving |

Salgenx Flow Battery: A Grid-Scale Energy Storage Solution Which Uses Saltwater Instead of Lithium |
Salgenx Flow Battery: A Grid-Scale Energy Storage Solution Which Uses Saltwater Instead of Lithium In an era where grid-scale energy storage is essential for the transition to renewable energy, Salgenx is proud to announce its Saltwater Flow Battery, a groundbreaking solution that eliminates the safety risks and environmental challenges associated with lithium-ion batteries.Designed with safety, sustainability, and scalability in mind, Salgenx batteries address key concerns such as fire hazards, toxic emissions, and operational costs, making them a superior alternative for large-scale energy storage. Salgenx Flow Battery: A Grid-Scale Energy Storage Solution Which Uses Saltwater Instead of Lithium
|

Advanced Electrolyzer Design Has Potential of Graphene (reduction of Graphite) and Cement Production (reduction of limestone without CO2 emissions) Simultaneously While Charging |
Fastest Path to a 3 MWh Grid-Scale Saltwater Flow Battery: Zinc-Chlorine vs NTP-Based Architectures Which saltwater flow battery chemistry reaches grid-scale commercialization first? This article compares zinc metal and NTP-based chlorine flow batteries across cost, efficiency, manufacturing complexity, and bankability to determine the fastest and most cost-effective path to a 3 MWh system.IntroductionGrid-scale energy storage increasingly demands systems that are safe, low-cost, scalable, and free from constrained materials. Saltwater flow batteries, particularly chlorine-based systems, have re-emerged as a compelling alternative to lithium-ion due to their use of abundant materials, non-flammable electrolytes, and long cycle life.Recent research has demonstrated a membrane-free chlorine flow battery architecture with exceptionally low projected material cost. Within this platform, two negative electrode strategies emerge as candidates for commercialization:1. Zinc metal negative enabled by a ZnCl2 additive2. NaTi2(PO4)3 (NTP) intercalation negative without zinc additiveThis article evaluates both approaches for a 3,000 kWh grid-scale containerized system and determines which offers the fastest, lowest-risk, and most cost-effective path to market.System Architecture OverviewBoth battery variants share a common core architecture:• Aqueous NaCl electrolyte• Chlorine redox at the positive electrode• Closed-loop chlorine handling using an immiscible organic carrier• Membrane-free stack design• Modular stacks arranged into a roughly 900 V DC busThe primary difference lies in the negative electrode chemistry and its implications for voltage, efficiency, manufacturing, and cost.Option A: Zinc-Chlorine Flow Battery with ZnCl2 AdditiveElectrochemistry• Positive: Cl2 / Cl minus• Negative: Zn2 plus / Zn metal• Nominal cell voltage: approximately 1.9 VAdding ZnCl2 to the electrolyte enables reversible zinc plating and stripping, replacing the need for a solid-state intercalation cathode.Manufacturing and Commercial Advantages• Zinc metal is a commodity material available as sheet, foil, or plated substrates (it is also available at Home Depot).• Electrode fabrication is simple and scalable• No high-temperature ceramic synthesis or vapor deposition steps• Aligns with historical zinc-halogen battery manufacturing experienceThe zinc electrode can be designed as a serviceable component, enabling predictable maintenance rather than end-of-life replacement.Risks• Zinc dendrite formation must be controlled through current density, flow design, and electrolyte management• Coulombic efficiency must be validated at scaleOption B: Chlorine Flow Battery with NTP CathodeElectrochemistry• Positive: Cl2 / Cl minus• Negative: NaTi2(PO4)3 (NTP)• Nominal cell voltage: approximately 1.8 VNTP is a NASICON-type insertion material offering good rate capability and stable cycling.Manufacturing and Commercial Challenges• NTP synthesis requires high-temperature calcination• Conductive carbon coating is necessary, typically involving additional thermal processing or vapor deposition• Powder processing and electrode fabrication add complexity and capital costWhile technically elegant, NTP introduces a more complex supply chain and slower ramp to volume production.Costed BOM Comparison for a 3 MWh ContainerUsing the Nature Communications estimate of approximately $5 per kilowatt-hour as a floor for active materials, and legacy zinc-chlorine plant data as a balance-of-plant sanity check, the following system-level costs emerge:• Zinc-Chlorine system total installed cost: approximately xxxxx dollars• NTP-based system total installed cost: approximately xxxxx dollarsThis corresponds to:• Zinc system: approximately xx dollars per kWh installed• NTP system: approximately xxx dollars per kWh installedIn both cases, balance-of-plant, power electronics, and safety systems dominate total cost, not the electrochemistry itself.Efficiency and Cost-Per-Delivered-kWhEfficiency must be evaluated alongside capital cost to assess true economic performance.• NTP-based systems have demonstrated laboratory-scale energy efficiency exceeding 90 percent• Zinc-based systems typically operate in the 70 to 75 percent range when system parasitics are includedWhen adjusted for efficiency:• Zinc system effective cost per delivered kWh: approximately xx to xx dollars• NTP system effective cost per delivered kWh: approximately xx to xxx dollarsThis indicates that while NTP offers higher efficiency, the zinc system compensates with lower upfront cost and faster manufacturability.Fastest Path to Market AssessmentFrom a commercialization standpoint, the decisive factors are manufacturability, supply chain simplicity, and execution risk.• Zinc metal electrodes eliminate the need for specialty ceramic powders and carbon coating processes• Anodes are already mass-produced industrial components• The zinc system supports a service-based maintenance model familiar to utilitiesThe NTP system, while attractive for future optimization, introduces additional process steps that slow time to first deployment.Commercial VerdictFor a first-generation, grid-scale saltwater flow battery:• The zinc-chlorine system with ZnCl2 additive is the fastest to market• It offers the lowest installed cost• It presents the least manufacturing risk• It enables early revenue and field validationThe NTP-based system is best positioned as a second-generation or premium offering once manufacturing scale and customer confidence are established.ConclusionSaltwater flow batteries based on chlorine chemistry present a credible, scalable alternative to lithium-ion for long-duration grid storage. Between the two leading negative electrode options, zinc metal offers the most direct path to commercialization for a 3 MWh containerized system. Its simplicity, cost advantage, and alignment with existing industrial practices outweigh the efficiency advantage of NTP in early deployments.A dual-track strategy is recommended: deploy zinc-based systems first to capture market share and operational data, while continuing development of NTP-based systems for future high-efficiency products.References1. Hou et al. High Energy and Low Cost Membrane Free Chlorine Flow Battery. Nature Communications, 2022.2. Detroit Edison and Energy Development Associates. Zinc Chlorine Battery Utility Study and Cost Analysis, 1976 to 1977.3. Bard and Faulkner. Electrochemical Methods Fundamentals and Applications. Wiley.4. U.S. Department of Energy. Grid Energy Storage Technology and Cost Characterization Reports.
|

|
Turn Brine Pools into Batteries Salton sea.Ocean water.Oil and gas producer water.Brine remediation.Powerplant cooling tower brine pool and boiler effluent use.Reverse osmosis (RO) and ion exchange waste/reject streams.Chlor-alkali and chemical plant waste.Acid rock and mine drainage.Food preservation and manufacturing waste streams.Desalination waste from potable water creation.Farming irrigation runoff.
|
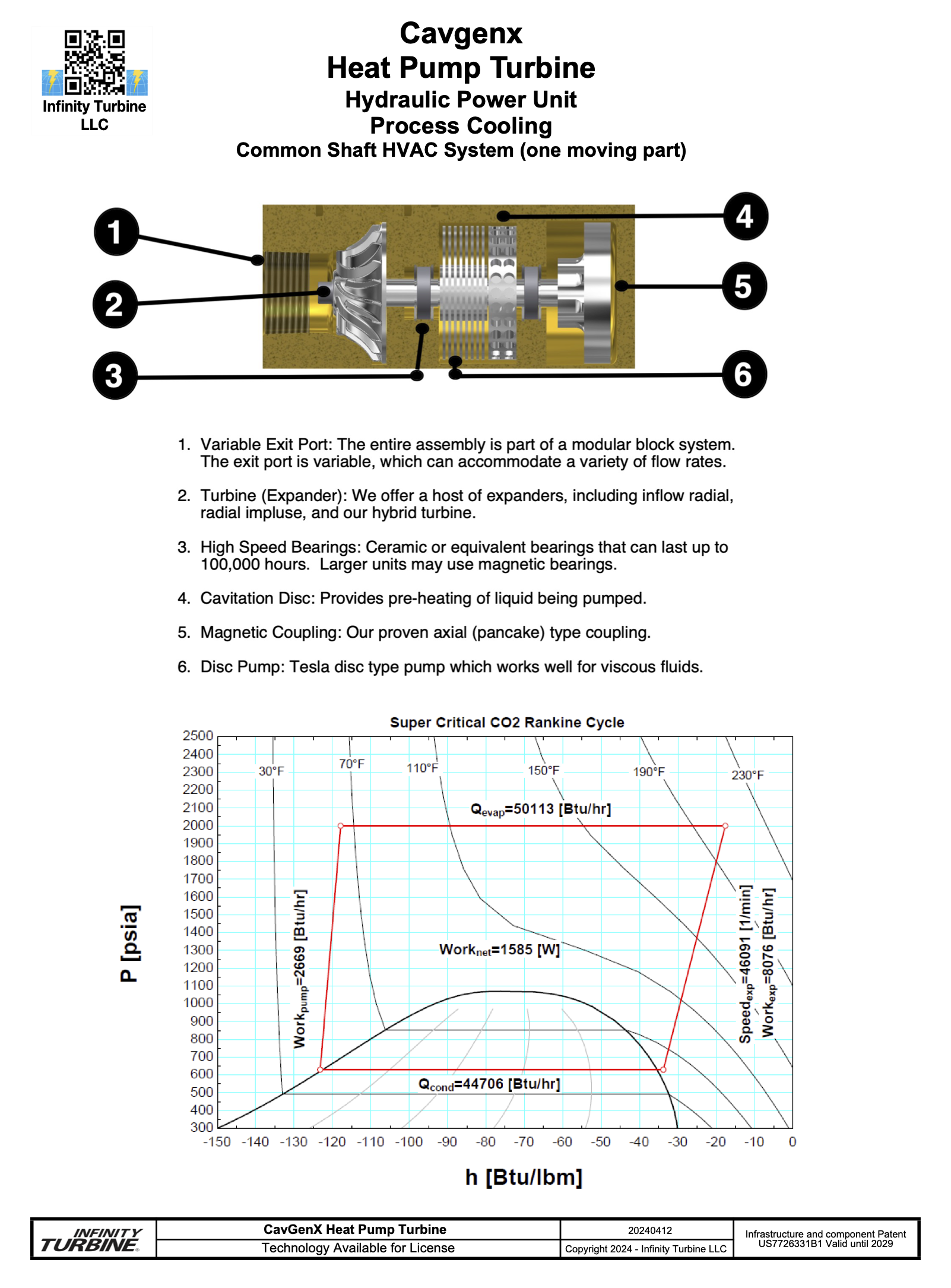
|
Heat Pump A heat pump is almost exactly like a ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle) system, which uses phase change to provide work to produce heat or cooling.In the case of a ORC system, the pressure reducing valve is replaced with an expander which mechanically rotates a electrical generator to make power.A heat pump has a high COP (Coefficient of Performance - is defined as the relationship between the power (kW) that is drawn out of the heat pump as cooling or heat, and the power (kW) that is supplied to the compressor) when compared to resistance heating.We have also been able to have a high COP with our cavitating discs in liquids that cavitate (water, CO2, and refrigerants).The advantage of a heat pump is that you can use off peak power to produce heating or cooling into a liquid, and then use that thermal resource during the on peak hours for huge cost savings. We term this utility grid price arbitrage.
|

|
Salgenx: Revolutionizing Energy Storage with Unmatched Innovation Salgenx, a groundbreaking leader in energy technology, has ignited excitement and disruption across the renewable energy sector. Much like DeepSeek, the AI startup that astonished Silicon Valley with its revolutionary AI models at a fraction of the cost, Salgenx has demonstrated transformative advancements in energy storage. Its proprietary saltwater battery technology offers unparalleled performance and scalability, delivering cutting-edge solutions at costs that redefine the economics of energy storage. CoT (Chain of Thought) is the reasoning model Salgenx developed to innovate and create leading-edge electrode technology.Salgenx is not just raising the bar—it’s reshaping the future of sustainable energy by making grid-scale energy storage more accessible, efficient, and eco-friendly than ever before. |

|
Salgenx AQUA LOGICx Battery Management System • AQUA-LOGIC (Adaptive Quantum Utility & Arbitration Logic for Saltwater Batteries)• AQUA-LOGIC is the intelligent control system for Salgenx saltwater batteries, optimizing power distribution, efficiency, and arbitration in energy storage. AQUA reflects the battery’s saltwater foundation, while LOGIC represents the system’s advanced decision-making and adaptability.Currently under development.
|

|
N.A.V.I.S. (Neural Adaptive Voltage & Intelligence System)NAVIS is the Hybrid Battery Management System (HBMS) that dynamically regulates energy flow, optimizing charge cycles, grid interaction, and arbitrage for maximum efficiency.• Neural Adaptive – AI-driven optimization for energy management.• Voltage – Precision control of charge and discharge processes.• Intelligence – Smart decision-making for grid integration and thermal storage.• System – A fully integrated software-driven energy management solution.Inspired by the Latin word for ship, NAVIS symbolizes fluid and adaptive energy control, effectively steering energy to where it’s needed most.Currently under development.
|

Plug and Play |
Saltwater Battery The Salgenx saltwater battery is a flow battery system, which requires two large tanks that hold fluid electrolytes. One tank is dedicated to salt water (add NaCL to water). The saltwater tank may be used for thermal storage.Fluids are circulated through electrodes, which regulate the input and output of electricity from the battery.The battery does not use a membrane, which is common on a redox flow battery.The absence of the membrane saves huge up front purchase costs, maintenance, and consumable expenses.The amount of electrolyte flowing in the electrochemical stack at any moment is rarely more than a few percent of the total amount of electrolyte present (for energy ratings corresponding to discharge at rated power for two to eight hours). Flow can easily be stopped during a fault condition. As a result, system vulnerability to uncontrolled energy release in the case of RFBs is limited by system architecture to a few percent of the total energy stored.The energy capacity is a function of the electrolyte volume and the power is a function of the surface area of the electrodes.
|

Plug and Play. NACS EV charging port available and Power Beaming. |
How it Works • Flow battery system which requires two large tanks that hold fluid electrolytes. One tank is dedicated to saltwater (just add NaCl to water). The saltwater tank may be used for thermal storage. The other tank is a liquid to store the separated NaCl.• Fluids are circulated through electrodes, which regulate the input and output of electricity from the battery. The Sodium (Na) is stored in the cathode materials.• No membrane. Electrolytes automatically separate. No membrane saves huge up-front purchase costs, maintenance, and consumable expenses.• Flow battery uses liquids (hence flow) so it takes 4-6 hours to charge or discharge. \• NaCl is split and stored separately, the energy can be stored for weeks or longer, unlike other flow systems. |

|
Summary of Tesla Megapack Lathrop Production Facility as of November 2023 In a November 16, 2023 interview on the Randy Kirk YouTube channel, Bradford Ferguson provided an update on Tesla's Megapack manufacturing. He visited Lathrop, California, and observed the production rate of Megapacks. In March 2023, he counted about 10 Megapacks produced per day. On a recent visit, he noted an increase to 27 per day, but estimated the actual rate to be around 18-19, occasionally dropping to 10 per day. The production capacity is believed to be 27 units per day, equating to 4 GW hours.Ferguson identified the primary production limitations as the availability of batteries and power electronics, specifically silicon carbide. Power electronics are crucial for converting DC to AC power and include devices like gallium nitride FETs and power diodes. The cost of batteries in each Megapack is around $300,000, with the total price of a 3 MWh Megapack being approximately $1.9 million.The interview concluded that with the resolution of battery and power electronics supply chain issues, Tesla could adopt a rapid expansion model for Megapack factories worldwide, potentially producing between 10,000 to 20,000 units annually. At full capacity (27 units per day), the output could reach 9,855 Megapacks (30 GWh) annually, yielding $18.725 billion in revenue and $9.362 billion in net profit. |
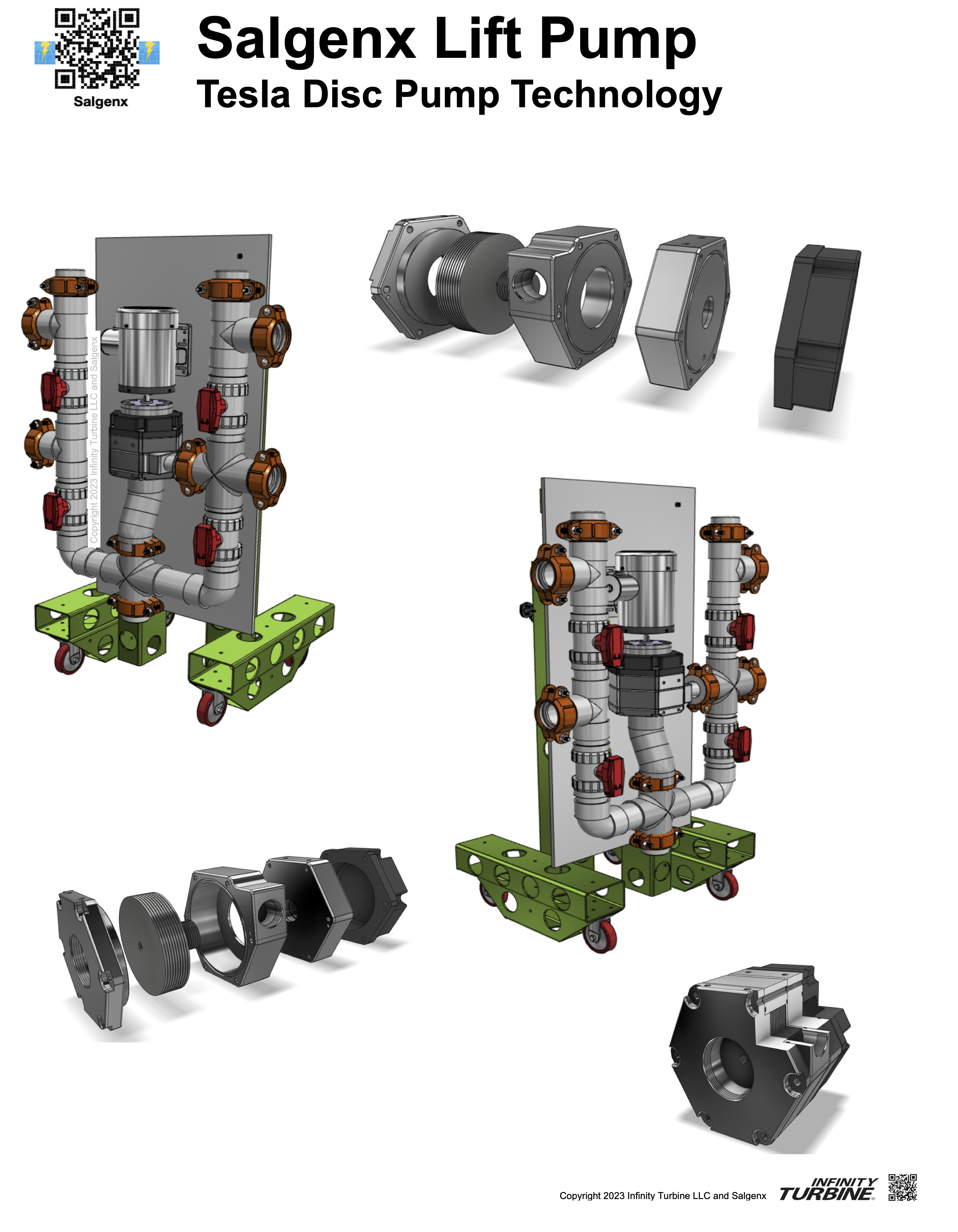
Salgenx Lift Pump System featuring Tesla disc pump technology for viscous fluids |
Salgenx Lift Pump System The Salgenx Lift Pump System is design to pump saltwater and viscous fluids.For the saltwater flow battery application, it has piping and fixtures which are electrolyte material compliant to resist corrosion from environmental conditions from saltwater.Each bulk liquid electrolyte tank will have a pump. Features: Each pump has a E-stop, Variable frequency Drive (variable flow depending on liquid), and sensor platform for manual and automated operation. The cart is a Infinity Caster Beam System with standard bolt-together assembly (by human or robot). The disc pump is a Patented modular block design driven by a magnetic coupling and stainless steel washdown motor. The pump is a modular bolt-together design for ease of maintenance and can be T-rack mounted for easy lift-in, lift-out servicing. The U manifold allows multi-port input/output/recirculation/services/sensor functions. The cart can easily be tipped slightly to transform into a hand cart for ease of movement through any standard door, hallway, or elevator. The unit can be mounted to any standard container. |
| CONTACT TEL: +1 608-238-6001 (Chicago Time Zone) Email: greg@salgenx.com | AMP | PDF | Salgenx is a division of Infinity Turbine LLC |