
PDF Publication Title:
Text from PDF Page: 002
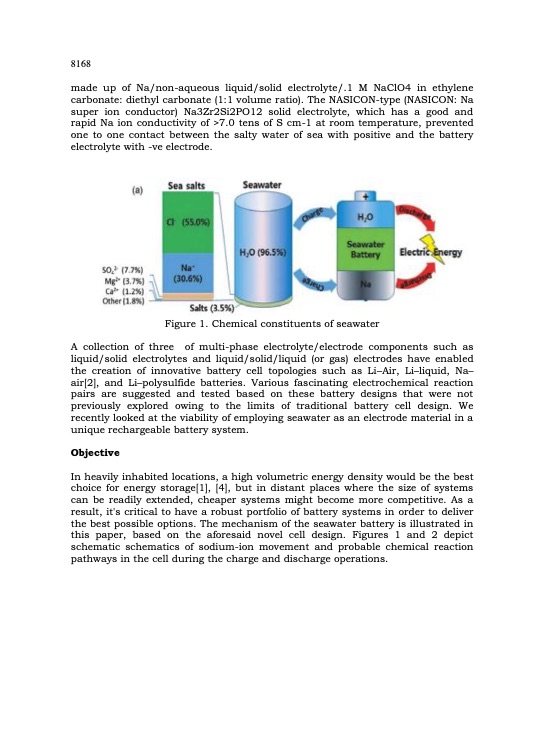
8168 made up of Na/non-aqueous liquid/solid electrolyte/.1 M NaClO4 in ethylene carbonate: diethyl carbonate (1:1 volume ratio). The NASICON-type (NASICON: Na super ion conductor) Na3Zr2Si2PO12 solid electrolyte, which has a good and rapid Na ion conductivity of >7.0 tens of S cm-1 at room temperature, prevented one to one contact between the salty water of sea with positive and the battery electrolyte with -ve electrode. Figure 1. Chemical constituents of seawater A collection of three of multi-phase electrolyte/electrode components such as liquid/solid electrolytes and liquid/solid/liquid (or gas) electrodes have enabled the creation of innovative battery cell topologies such as Li2Air, Li2liquid, Na2 air[2], and Li2polysulfide batteries. Various fascinating electrochemical reaction pairs are suggested and tested based on these battery designs that were not previously explored owing to the limits of traditional battery cell design. We recently looked at the viability of employing seawater as an electrode material in a unique rechargeable battery system. Objective In heavily inhabited locations, a high volumetric energy density would be the best choice for energy storage[1], [4], but in distant places where the size of systems can be readily extended, cheaper systems might become more competitive. As a result, it's critical to have a robust portfolio of battery systems in order to deliver the best possible options. The mechanism of the seawater battery is illustrated in this paper, based on the aforesaid novel cell design. Figures 1 and 2 depict schematic schematics of sodium-ion movement and probable chemical reaction pathways in the cell during the charge and discharge operations.PDF Image | Electric lantern using sea water
PDF Search Title:
Electric lantern using sea waterOriginal File Name Searched:
electric-lantern-sea-water-battery.pdfDIY PDF Search: Google It | Yahoo | Bing
Product and Development Focus for Salgenx
Redox Flow Battery Technology: With the advent of the new USA tax credits for producing and selling batteries ($35/kW) we are focussing on a simple flow battery using shipping containers as the modular electrolyte storage units with tax credits up to $140,000 per system. Our main focus is on the salt battery. This battery can be used for both thermal and electrical storage applications. We call it the Cogeneration Battery or Cogen Battery. One project is converting salt (brine) based water conditioners to simultaneously produce power. In addition, there are many opportunities to extract Lithium from brine (salt lakes, groundwater, and producer water).Salt water or brine are huge sources for lithium. Most of the worlds lithium is acquired from a brine source. It's even in seawater in a low concentration. Brine is also a byproduct of huge powerplants, which can now use that as an electrolyte and a huge flow battery (which allows storage at the source).We welcome any business and equipment inquiries, as well as licensing our flow battery manufacturing.| CONTACT TEL: 608-238-6001 Email: greg@salgenx.com | RSS | AMP |