
Lithium Ion Battery Fire and Explosion
|
|

Lithium Ion Battery Fire and Explosion |
|
Grid Scale Storage Publications Search
Search Lithium Fire Publications search was updated real-time via Filemaker on:
Search Lithium Fire Publications | Return to Search ListSearch Completed | Title | Lithium Ion Battery Fire and Explosion
Original File Name Searched: 8-375.pdf | Google It | Yahoo | Bing
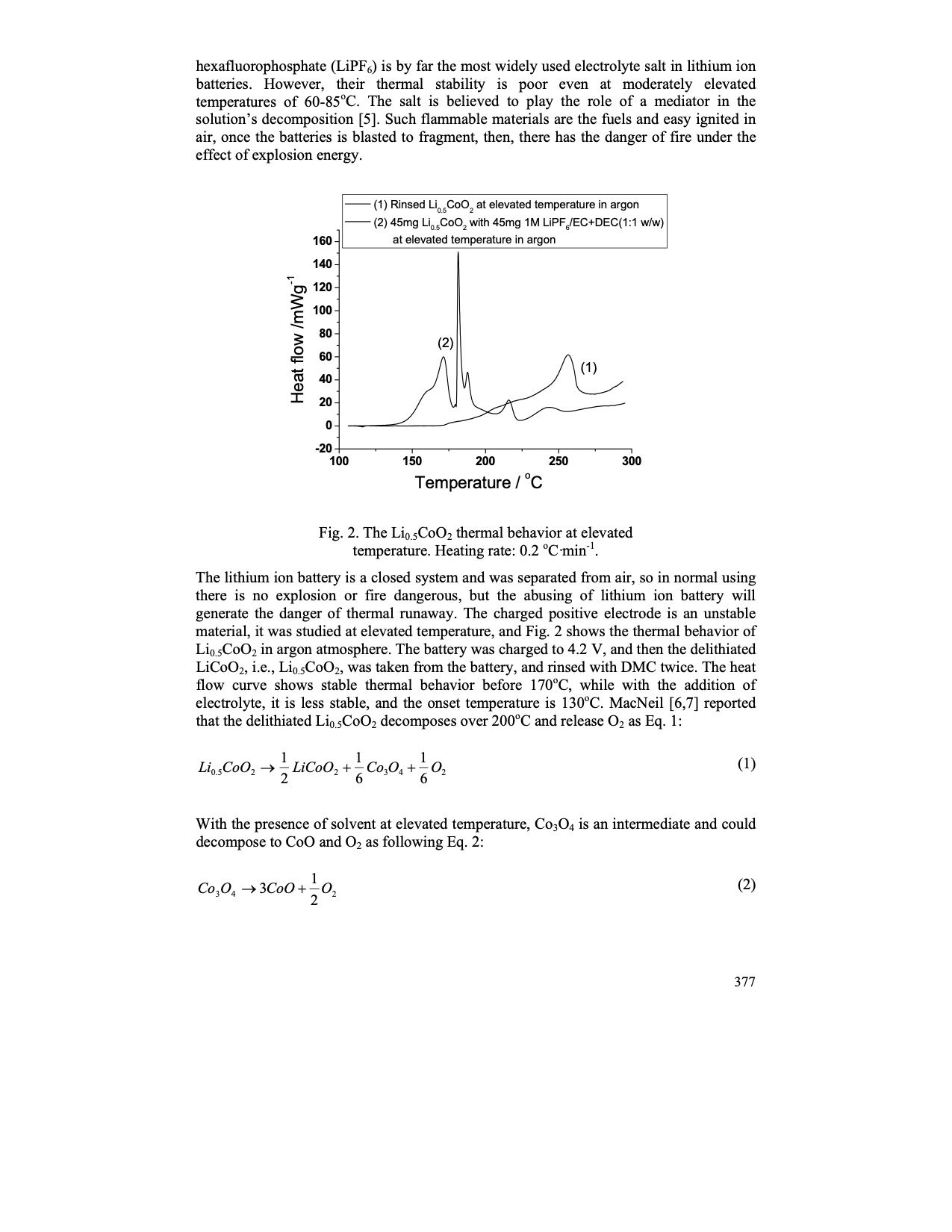 Page | 003 hexafluorophosphate (LiPF6) is by far the most widely used electrolyte salt in lithium ion batteries. However, their thermal stability is poor even at moderately elevated temperatures of 60-85oC. The salt is believed to play the role of a mediator in the solution’s decomposition [5]. Such flammable materials are the fuels and easy ignited in air, once the batteries is blasted to fragment, then, there has the danger of fire under the effect of explosion energy. |
Search Contact: greg@salgenx.com